Cost Reduction at a Silicon Thin Film Solar Cell Mass Production Line
Due to the pressure for cost reduction in a thinfilm PV production line an effort to reduce the running cost of the waste gas treatment systems was started.
As a precondition the DRE (Destruction Removal Efficiency) should not be reduced. Intended improvements for maintenance and media consumptions were tested on-site under production conditions over a 6‑month time frame.
Overview of the thinfilm PV production line at Baoding Tianwei
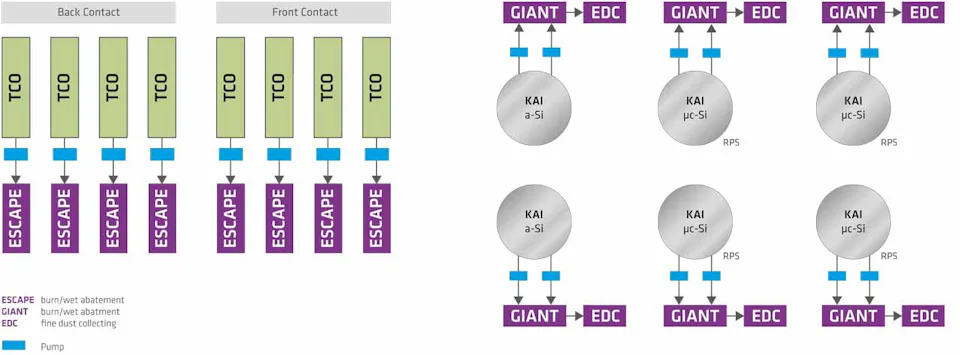
The a‑Si/μc-Si CVD-process tools use large amounts of SiH4, H2, NF3 and TMB, PH3 as doping gases. The process gases are pyrophoric, explosive or harmful to the environment. Therefore the process exhaust is treated by combustion and wet scrubbing point-of-use abatements in connection with wet electrostatic dust collectors. Each day approximately 100 kg of SiO2 dust and 180 kg of HF are generated and retained in the abatement systems. The exhaust gases from the TCO tools contain DEZ, ZnO particles and hydrocarbons. Each TCO tool is connected to a burn/wet waste gas treatment system which oxidizes combustible compounds and retains particles.
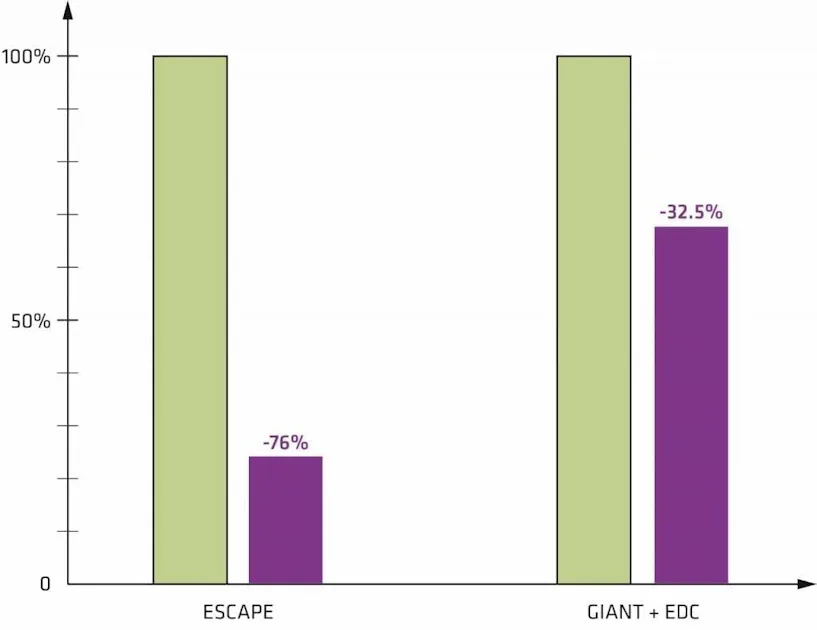
Cost Reduction Maintenance: Main causes and achieved improvements
KAI — Waste gas treatment with GIANT/EDC
Particle deposits in the reactor and connection pipe to electrostatic dust collector
Deposits in the reactor were much less than expected → maintenance interval extended
Added a self-cleaning and maintenance free pre-filter to the connecting pipe → no more maintenance of the connection pipe required
Sedimentation of particles in the circuit tank → prevented by increased circulation/agitation of the washing fluid
Salt scaling turned out the main cause of problems → completely eliminated by small changes in the tank
ESCAPE — Maintenance intervals before beginning of testing: same as for TCO tools
Observed very small particle deposits during maintenance
Measure: maintenance intervals extended
Result: no negative impact on uptime
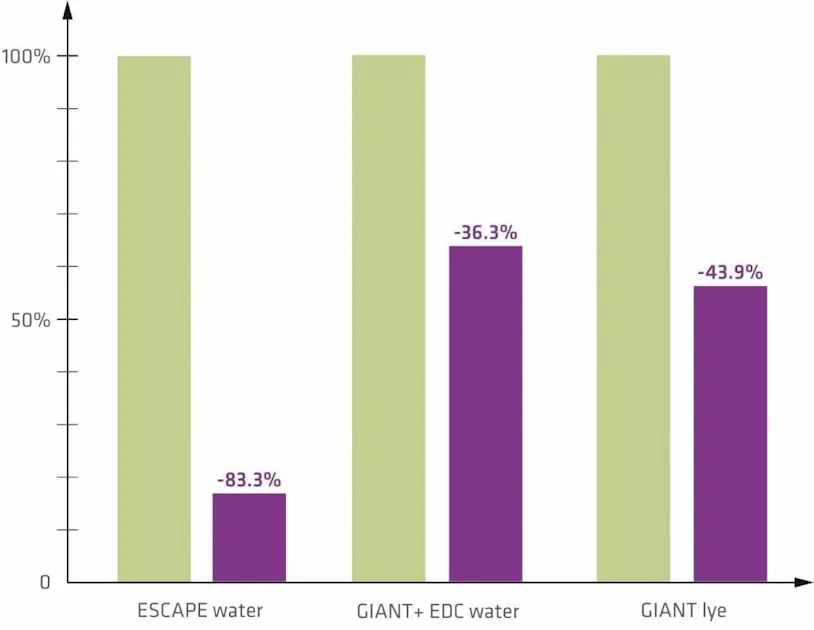
Utility Savings at point-of-use waste gas treatment
Waste Gas Treatment System GIANT
Optimization of pH regime → reduced lye consumption
Prevention of sedimentation and improved filtration of the scrubbing liquid → higher concentration of particles in the liquid possible, reduced water consumption
Waste Gas Treatment System ESCAPE
Reduced water consumption → no negative impact
Your Contact Person for all Questions on Waste Gas Treatment
For customized abatements for safe waste gas treatment in the solar industry
Chief Business Development Officer