Chemical-physical Water Treatment Plant for a Leading High-tech Manufacturer
A leading silicon wafer manufacturer expands with a new DAS water treatment plant. The system efficiently treats complex wastewater while cutting energy and operating costs.
Importance of Water Treatment in the Semiconductor Industry
Water treatment and purification play a crucial role in semiconductor manufacturing, particularly in silicon wafer production. Nearly all production steps require ultra-pure water (UPW), as even the slightest impurity can compromise wafer quality and functionality. At the same time, the process generates large volumes of wastewater containing chemicals and particles. Efficient wastewater treatment and water purification are therefore essential to ensure product quality, meet environmental standards, and promote sustainable resource use.
Semiconductor manufacturers employ energy-efficient treatment systems to optimise water consumption during wafer production. Process-integrated methods such as precise pH control, particle retention, and selective ion separation help minimise chemical waste and reduce wastewater pollution. These measures ensure compliance with strict environmental regulations, including those defined in the EU Industrial Emissions Directive. Manufacturers also benefit economically, as sustainable water treatment saves resources and lowers operating costs. Environmentally responsible wastewater management is a central pillar of the industry’s environmental strategy and a key element of ISO 14001 certification.
About the Customer
The high-tech manufacturer ranks among the world’s top silicon wafer producers and offers a comprehensive portfolio. As a technological pioneer, the company plays an integral role in the global semiconductor value chain, supplying producers of MEMS, sensors, high-frequency and power devices.
The company relies on certified management systems and sustainable production principles. It holds ISO 14001:2015 certification and continuously strives to minimise the environmental impact of wafer manufacturing while ensuring efficient use of resources. Water consumption and recycling are key areas of focus.
Project Overview
The customer plans to increase its production capacity and has therefore built a new fab expansion. This is accompanied by the expansion of the wastewater treatment plant. DAS Environmental Experts (DAS EE) has designed, built and commissioned a water treatment plant to treat specific wastewater streams generated during wafer production in clean rooms. The three wastewater streams are
Weak Hydrogen Fluoride (WHF): fluoride-containing water
Silica Waste Drain (SWD): silicon-containing water
Weak Waste Acid (WWA): water with an acidic pH value
The contract aimed to establish three independent treatment lines for removing fluoride and silicon and adjusting the water’s pH value.
The treatment lines are designed for high-volume flows. In fluoride treatment and silicon removal, the throughput at full load is 40 m³/h for each process, while the neutralisation line can process 200 m³/h. The entire plant is designed as a free-flowing system and uses only hydrostatic pressure, eliminating the need for additional pumps. This significantly reduces energy consumption and increases ease of maintenance.
The hydraulic height differences are utilised optimally, and the use of lamella clarifiers ensures efficient solids separation. The plant is controlled and monitored by a DAS EE control system, which enables programming and visualisation via a touch panel (human-machine interface, HMI). All plant functions can be operated and controlled centrally via this panel.
Project Development
As part of the project planning, a detailed schedule was developed to outline the entire process, from the initial water sampling to the final system commissioning. The first water samples were taken during the early project phase. These samples were essential for preparing the technical proposal and subsequent presentation to the customer.
The official project start (Month 1) marked the beginning of implementation according to a project plan jointly prepared in advance. Cooperation with the construction site operator intensified, while supplier inquiries were initiated to ensure the timely delivery of all required components. The main contract defined clear responsibilities, particularly concerning the technical equipment, which required close coordination with other involved trades. A major focus at this stage was the detailed design of the equipment and the precise definition of all technical requirements.
Several follow-up meetings were conducted on site at the customer’s facility to regularly monitor construction progress. A key milestone was reached when the building became ready for equipment installation. From Month 6 onwards, the construction manager from DAS EE coordinated the entire installation process on site, marking the transition from planning to implementation.
Construction was scheduled for completion by Month 10. By this stage, all installations had been completed, and the first signal tests, particularly in the electrical and software systems, were successfully executed. The so‑called “cold commissioning” phase also began around this time, during which the functionality of the entire plant was thoroughly tested using clear water. This test phase lasted approximately four weeks.
The next major project step, “warm commissioning,” took place once the new production facility was ramped up in a subsequent project phase (around Month 15). During this stage, process water was used for the first time to fine‑tune the system and ensure smooth operation under real manufacturing conditions. Warm commissioning was successfully completed by the end of that phase, and the system was officially handed over to the customer.
The carefully coordinated schedule enabled efficient management of all work steps and ensured that the customer’s high quality and reliability standards were fully met.

Challenges and Solutions
Time Management
One of the biggest challenges during the project was managing time effectively. The tight schedule required forward thinking and quick decision-making from the outset. For example, the necessary containers were ordered immediately after the official project start to compensate for delivery times and avoid delays. Nevertheless, external factors led to the kind of logistical challenges that are typical of large-scale projects. The DAS team on site resolved these challenges with great dedication. These efforts enabled the project to be completed on schedule.
Technical Challenges
From a technical perspective, the planned dimensions of the system presented a particular challenge as they did not always align with the available on-site space. To make optimal use of the available space, the planning had to be continuously fine-tuned and there had to be close cooperation with all the contractors involved. This enabled the system to be tailored to the local conditions, despite the tight space constraints. Making consistent use of the entire room height kept the required floor space to a minimum, using the available space particularly efficiently.
Manufacturing the control cabinets was another key issue. Experience gained from previous projects helped to avoid common errors, but the new dimensions — five main control cabinets and one remote in/out (RIO) — necessitated close collaboration between the DAS teams in Dresden and at the customer’s site. Synergy effects between the Water and Gas Business Units enabled valuable lessons to be learned and the quality of the sophisticated control cabinets to be improved further.
As production ramped up at the new fab, fluctuating wastewater volumes made it difficult to adjust the dosing technology precisely. To ensure stable process control, the dosing was continuously adjusted to the varying volume flows. The very low pH value in the fluoride plant area presented a challenge in terms of designing the measurement technology and selecting suitable suppliers who could measure reliably under these specific conditions.
During the flocculation and sedimentation process, DAS EE carried out extensive laboratory tests to optimise the dosage preparation. The dosage quantities were validated to enable successful adjustment of the chemical addition even with fluctuating wastewater quantities. The calcium addition is specifically adjusted according to the actual requirement by measuring the fluoride content in the wastewater. Using calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂) and calcium chloride (CaCl₂) together allows the amount of chemicals to be optimally controlled. This results in more efficient use of the substances and reduces ongoing operating costs.
Coordination
Coordinating the construction site presented a challenge due to the large number of contractors working in parallel. In this context, DAS EE’s experience of working on complex construction sites was invaluable. Smooth cooperation with other trades was a key factor in the project’s success. For instance, central components such as tanks and lamella clarifiers were manufactured by a local contractor recommended by the customer who had previously worked on other projects for the customer. The construction plan was drawn up through close collaboration between the DAS EE site manager, the customer’s project manager, and the site operator. A detailed project schedule was available by the time the tender was issued, and this was based on experience and took into account the high level of coordination required with the customer.
Documentatioin and Change Management
Careful change management ensured that the project progress was documented in a transparent and comprehensible manner. Even the slightest modifications to the project were recorded in detail and incorporated into the technical descriptions and operating instructions. This level of detail in the project plan led to thorough elaboration, enabling additional components to be successfully integrated and existing solutions to be optimally adapted. Consistent documentation guaranteed that all changes could be traced at every stage and that the system’s quality and functionality were always assured. The experience gained and the solutions developed during the project contributed significantly to meeting the high quality, deadline and functionality requirements.
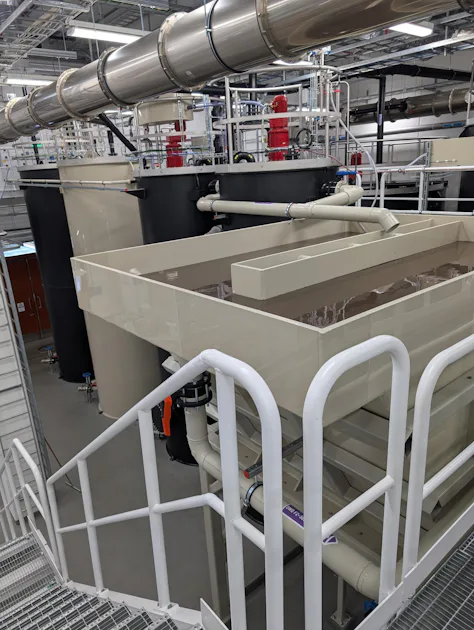

Summary
The collaboration between DAS Environmental Experts and the customer is founded on a long-standing and trusting partnership. The high-tech company has gained extensive knowledge of the functionality and reliability of DAS products for waste gas treatment in semiconductor manufacturing through several jointly implemented projects. DAS EE’s Business Unit Water has convincingly demonstrated its expertise in planning, constructing and commissioning large-scale water treatment plants through successfully completed reference projects.
A Milestone for Sustainable Semiconductor Manufacturing
The expansion of the wastewater treatment plant is another significant milestone in this collaboration, and it can serve as a reference for future large-scale semiconductor industry projects. Despite tight deadlines and complex technical requirements, the plant was completed on time and to a high standard. This involved developing and integrating three independent treatment lines for different wastewater streams, using innovative control and measurement technology, and consistently using existing resources to improve energy and cost efficiency. The following aspects can be considered decisive:
Early and detailed planning. Close integration between the planning and execution phases was crucial in avoiding time losses due to delivery bottlenecks or interface problems.
Flexibility in system planning. Through continuous adjustments to local conditions and utilisation of the room height, the system could be optimally integrated into the existing infrastructure.
Synergy effects through interdisciplinary cooperation. Close collaboration between the DAS teams in Dresden and at the customer’s site, as well as between the Water and Gas business units, has resulted in valuable learning outcomes and improved plant quality.
Innovative dosing and measurement technology. Stable process control was achieved despite fluctuating wastewater volumes thanks to targeted, demand-based chemical dosing based on continuous measurements, which also reduced operating costs in the long term.
Efficient Change Management: Complete documentation and transparent communication of all adjustments ensured the traceability and quality of the entire project.
Investing in modern water treatment is a significant milestone for the sustainable expansion of semiconductor manufacturing. The customer’s forward-looking production technology is setting new industry standards. Its close collaboration with DAS Environmental Experts and local partners demonstrates how technological excellence and sustainability are shaping the future of semiconductor production.
Would you like to learn more about our wastewater treatment offerings?
Our Environmental Experts look forward to hearing from you.
Director Sales Water Treatment High Tech Industries