Biological Wastewater Treatment
Comprehensive know-how coupled with numerous successfully implemented customer projects – the biological aerobic & anaerobic treatment of wastewater has been part of DAS EE's core business for over 15 years.
Flexible Biological Treatment Processes for a Wide Range of Industries
Thanks to our comprehensive portfolio of biological, aerobic and anaerobic wastewater treatment processes, we can tailor each plant precisely to the individual conditions of our customers. This enables us to develop tailor-made, high-performance and resource-efficient solutions for sustainable industrial wastewater treatment.
Our biological processes are used successfully worldwide in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries, semiconductor production and in the energy sector. They have also proven themselves in the pulp and paper industry, in laundries and textile production as well as in food processing and agriculture. Wherever high organic loads need to be reduced safely, economically and in an environmentally friendly manner, biological processes offer the optimum solution.
Functionality & Use of Biological Wastewater Treatment
The biological treatment of industrial wastewater makes it possible to effectively remove organic wastewater constituents such as proteins, fats and sugars as well as ammonium and nitrate contamination from industrial wastewater. With the help of billions of microorganisms, the substances dissolved in the wastewater are converted into a solid, settleable biomass during biological treatment. This is separated from the water by sedimentation in a subsequent process and then partially returned to the treatment process.
After biological treatment, the purified water can be returned to watercourses or reused in the production process with appropriate further treatment without any adverse effects on the environment.
Biological-Aerobic and Anaerobic Wastewater Treatment
In the biological treatment of wastewater, a distinction is made between two main types of processes: the aerobic and the anerobic process. The distinction is very simple. While the use of oxygen is necessary for aerobic wastewater treatment, this is not required for the anerobic process.
Both variants have some clear advantages and disadvantages, which must be taken into account depending on customer requirements. While aerobic treatment usually results in less odor nuisance and nutrient removal is often more effective, oxygen enrichment and the disposal of biomass can result in significantly higher overall energy consumption and increased operating and maintenance costs.
Anerobic wastewater treatment processes are often cheaper and more flexible, and the biogas produced can be used as a source of renewable energy. However, it is not uncommon for both wastewater treatment processes to be used in one wastewater treatment plant in order to ensure energy and cost-efficient treatment in compliance with the respective regulatory requirements for discharge.
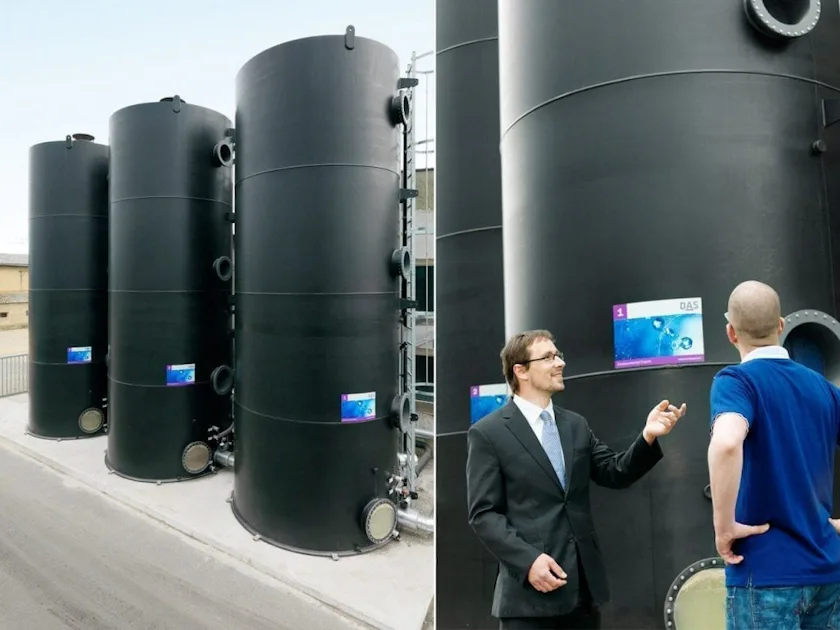
MBBR Process (Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor)
Flexible, reliable and economical to operate – DAS complete solutions for biological wastewater treatment using the MBBR process
The MBBR process (fluidized bed process) is a technology for biological wastewater treatment. In this process, microorganisms are cultivated as a biofilm on a carrier material. These microorganisms are responsible for the degradation of both organic wastewater constituents and nitrogen compounds. Due to the microorganisms living in biofilms, the MBBR treatment process is very robust and much more stable than other biological treatment technologies.
As with other biological processes, excess sludge is also produced during wastewater treatment with MBBR bioreactors. However, the quantity is significantly lower than in conventional activated sludge processes with a similar capacity. Nevertheless, the treated wastewater usually has to be separated from the resulting sludge after treatment in the MBBR. This can be done in a secondary clarifier by sedimentation, for example. In the case of indirect discharge into another wastewater treatment plant, it is also possible to consider dispensing with sludge separation if the capacity and design of the wastewater treatment plant permit this and undesirable sedimentation processes on the transport route can be ruled out.
It is also possible to use the fluidized bed process anaerobically - in this case, mixing takes place with the aid of pumps or an agitator.
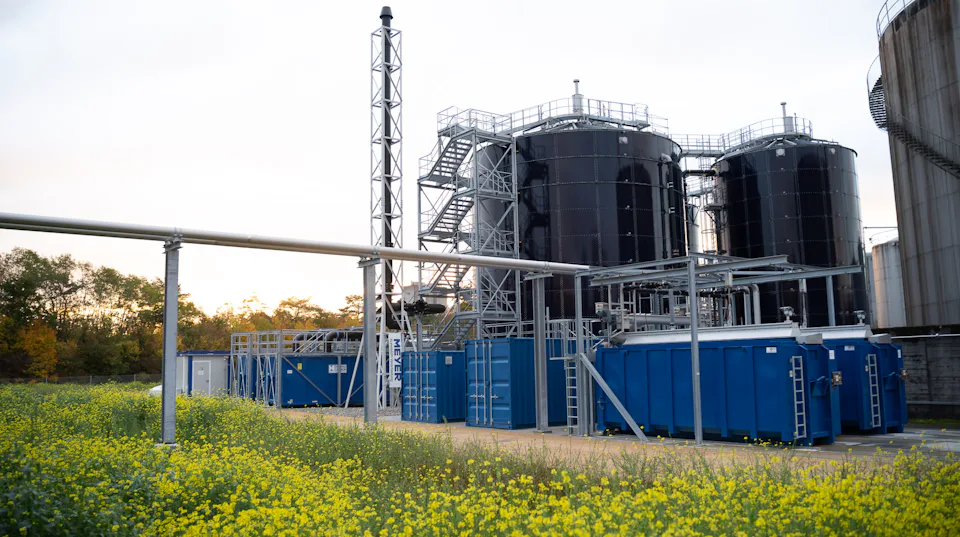

All MBBR Systems offer the Following Advantages:
Compact biological treatment process
High performance
Simple operation
High stability even under difficult operating conditions
Low amount of excess sludge
No recycling of biomass
The thickness and composition of the biofilm on the carrier material are influenced both by the shear forces prevailing in the bioreactor and by the substances contained in the wastewater: the higher the content of organic substances in the wastewater, the faster the biofilm grows. Activated sludge processes have the disadvantage that when excess sludge is removed, some of the microorganisms present in suspension are also regularly removed.
Despite the return of recirculation sludge from secondary clarification, the microorganisms only reach a relatively short age overall. In the MBBR process, the immobilized microorganisms on the carriers can have a much longer lifespan. This allows microorganisms to establish themselves in the biofilm that have specialized in compounds that are difficult to degrade but have very long generation times. Overall, the stability of the purification process is higher than in activated sludge systems, and load peaks are better absorbed.
DAS Environmental Expert GmbH uses a carrier material that has a very high specific surface area and therefore enables particularly compact MBBR bioreactors. The shape of the packing also reliably prevents the carrier material from blocking and achieves a consistently high degradation rate. Our MBBR systems can be designed as compact systems or as modular bioreactors. The modular reactors require significantly less space than conventional activated sludge plants. There is no need for civil engineering work. With the appropriate process engineering design, our MBBR can even be designed and operated as a denitrification reactor.
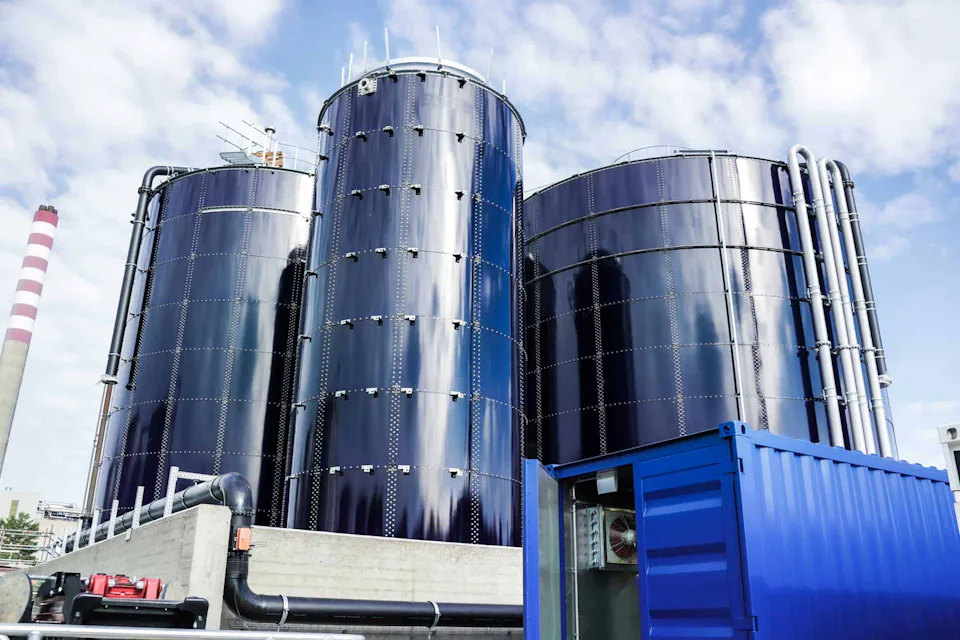
SALVINIA – Scalable MBBR Reactors in Four Standard Sizes
In the product group SALVINIA we combine efficiency and compactness with time and cost benefits for our customers. The MBBRs are available in four standard sizes SALVINIA 70, SALVINIA 170, SALVINIA 470 and SALVINIA 1060 can be used in a variety of ways in all industries for the biological treatment of industrial wastewater.
Further Processes for biological Treatment
Biological Wastewater Treatment with the Membrane Bioreactor (MBR)
The membrane bioreactor (MBR) can also be used for the oxidation and nitrification of organic substances in wastewater. The pollutant degradation takes place in an aerated aeration tank with a very high sludge concentration. In this reactor, the clarified wastewater is separated from the activated sludge using membranes via ultrafiltration. Such a membrane filter module can also be integrated submerged into existing biological treatment stages; however, a separate reactor is much easier to maintain.
Questions about biological wastewater treatment?
We can advise you on aerobic and anaerobic processes and find the right solution for your wastewater flow. Please do not hesitate to contact us.
Deputy Chief Operating Officer Water Treatment



