TSUGA: From a Master Thesis to a Successful DeNOx Solution
In semiconductor production, the effective removal of nitrogen oxides (NOx) is of crucial importance. These harmful compounds are produced during the production process and pose a significant risk to the environment and health. DAS Environmental Experts supports its customers with innovative solutions for the efficient purification of these harmful waste gases.
DeNOx is a process used to remove nitrogen oxides that are produced during semiconductor production and the subsequent purification of process gases in the subfab. Nitrogen oxides are harmful compounds that endanger the environment and people. The DeNOx process consists of using a catalyst and a reducing agent to absorb or chemically convert nitrogen oxides from the gases before they are released into the atmosphere. This helps to reduce environmental pollution.
DAS Environmental Experts (DAS EE) first tackled the problem of efficient nitrogen treatment in semiconductor production back in 2017 and quickly developed TSUGA, a stand-alone solution for secondary waste gas purification. What initially began as a Master Thesis as part of an internal development project quickly spread. In collaboration with the outstanding research ecosystem in Saxony, in particular with the support of Technical University Dresden and Technical University Bergakademie Freiberg, the Research & Developern team at DAS EE focussed on methods for more efficient waste gas treatment using a secondary abatement system that can be connected downstream of waste gas purification systems such as burn-wet systems.
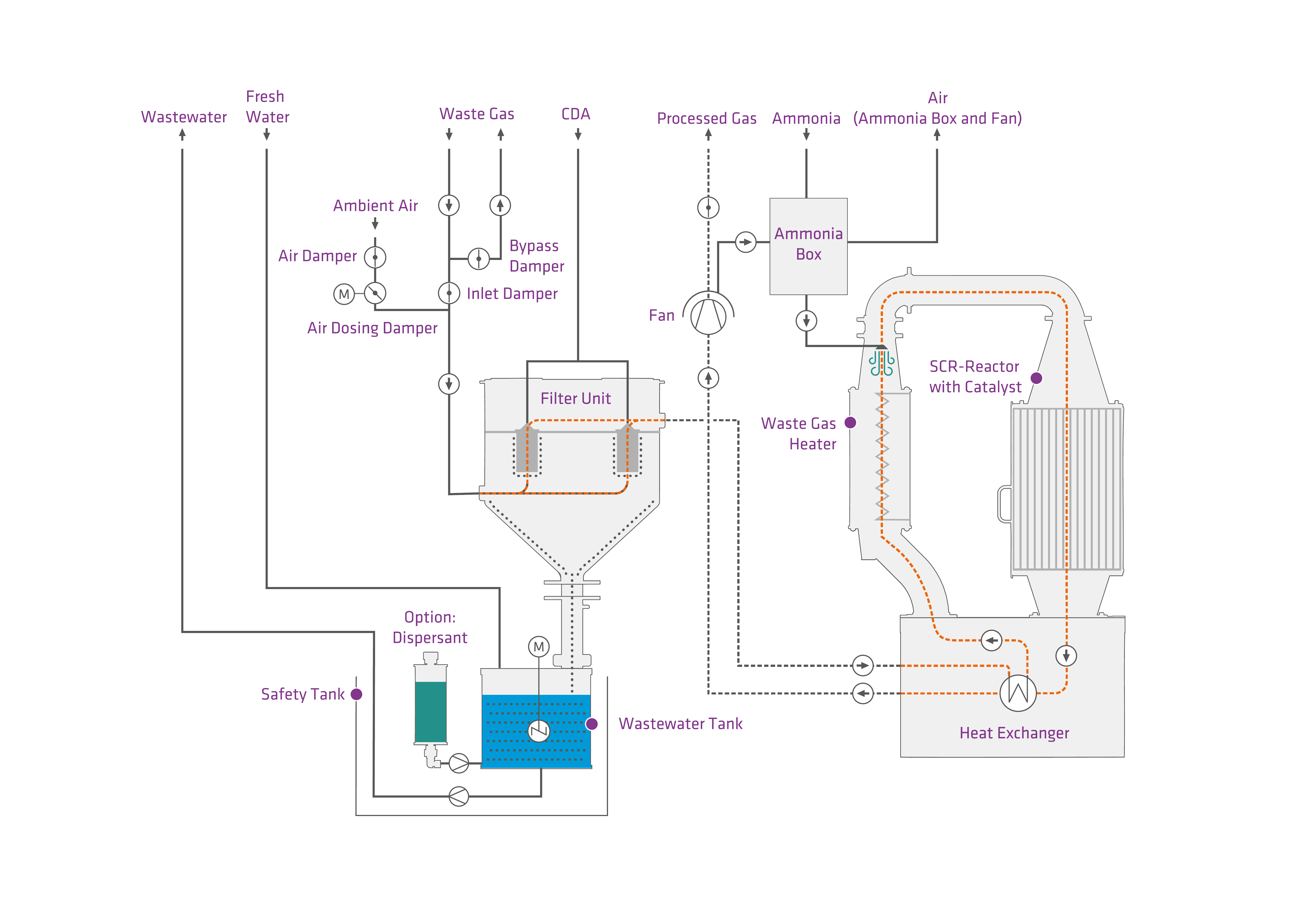
Experimental Setup
In a first step, a simplified laboratory system with an upstream dust filter was built. The system is based on selective catalytic reduction (SCR) using ammonia. The waste gas stream from semiconductor production is first treated in a burner scrubber system using the integrated combustion process and then washed out. In the next step, the already treated waste gas is channelled through a highly effective membrane filter in the downstream DeNOx system into the SCR reactor, where it is mixed with ammonia (NH3) as a reducing agent and heated to a temperature in the range of 180 °C — 300 °C. It then flows through a honeycomb catalytic converter in which the reduction with ammonia into nitrogen and water vapour takes place.
The diagram opposite shows the functional principle of the TSUGA.
High Reduction Efficiency
The system achieves a very high reduction efficiency of up to 95% for NOx and an impressive efficiency of up to 99.9% for the total dust content. The treated gas can then be safely released into the environment. Several factors contribute to these outstanding values, first and foremost the specially designed SCR reactor, which has to be both compact and highly efficient. Thanks to the sophisticated adjustment of all parameters such as the admixture of ammonia, the correct temperature selection and the optimum utilisation of process heat, TSUGA achieves the efficiency values mentioned with comparatively low additional energy requirements and low ammonia slip. At the same time, the integrated particle filter ensures maximum protection of the catalytic converter.
A number of other student theses dealt with further possibilities for process optimisation, in particular by developing a concept for efficient control based on the online measurement of reduction efficiency and ammonia slip. Comprehensive tests were also carried out in order to be able to evaluate the interaction of the components in the system under conditions that are as close to reality as possible. In addition to the efficiency of the system in terms of separation and heat recovery, the focus was on the stability of operation with regard to the sensitive pressure requirements.


From Laboratory Project to Pilot Plant
In 2021, this approach met with great interest from a well-known semiconductor manufacturer that was looking for innovative solutions to significantly reduce its nitrogen oxide emissions. DAS EE was known to the company as a long-standing, reliable provider of environmental technology solutions. In close collaboration with this customer, the laboratory project was turned into a pilot plant within just six months, which was subjected to an initial endurance test in the manufacturer’s subfab in 2022. By quickly adapting the technology to the customer’s specific requirements, DAS Environmental Experts was able to demonstrate the performance of the then still nameless test system.
An unexpected challenge was that the SCR system, which has since been given the name TSUGA*, was not — as initially assumed — to be connected downstream of DAS EE’s burn-wet systems, but rather downstream of the systems of another supplier. By making the necessary adjustments to the test plant to suit the process gas volume flow and other specifics of the upstream process, the environmental experts gained valuable experience that allowed TSUGA to be variably adapted to different process sequences.
Technical Specifications
DeNOx: SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) with Ammonia
- High reduction efficiency regardless NOx source: up to 95% **
- Low NH3 slip: 10 ppm by precise control of the dosed reducing agent **
- Flexible solution for NO and NO2 in broad concentration ranges up to 4000 ppm at total volume flow of up to 5000 slm
- Low energy demand: low temperature process and energy recovery by heat exchanger
DeDust: Membrane Filter (Surface Filtration)
- Necessary pre-treatment for catalyst
- High reduction efficiency of PM2.5, PM10, total dust fraction (up to 99.9%)
- Applicable for typical post-combustion PM pollutants
** Tradeoff between NOx DRE and NH3 slip: Increase of DRE will result in increase of slip and vice versa.

This quick system development was made possible by the excellent cooperation between the two DAS Business Units Gas (BUG) and Water (BUW). The water business is traditionally a project business in which precise customer specifications have to be realised in a defined location within a specified time frame. This specific form of project management was successfully applied to the rapid further development of the laboratory plant into a mature customer product. The joint effort was rewarded: even before the pilot project was completed, DAS EE received an order for additional TSUGA systems optimised for high-volume manufacturing (HVM).
DAS EE is proud of the great trust placed in it by its customer — an impressive testimony to our successful work in the development of intelligent environmental solutions!
Good to know:
Like all DAS product names, the name *TSUGA comes from botany and refers to the genus name of the hemlock tree, whose main characteristics are durability and resistance to moisture.
