Optimal Aeration of Wastewater Engineering Plants
For the aerobic decomposition of organic or oxidizable substances in wastewater, oxygen is required, which can be introduced into the wastewater by means of compressed air. In addition to supplying the required oxygen, systems for wastewater aeration can also have the task of mixing wastewater and sludge or preventing deposits in the basin.
In addition, aeration measures for wastewater treatment plants increase the operational safety and the degradation performance of the system. The aim of aeration is always to achieve a rapid phase transition of the oxygen from gaseous to liquid. This can be achieved by an increased oxygen concentration in the air mixture or by a mechanical solution that produces an optimal bubble size.
Flexible Wastewater Aeration with Jet Aerators
Jet aerators are ideal for use in MBBR (Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor) or activated sludge plants. They are also the preferred choice when the wastewater treatment task is to dispose of lime as well as large solids and sludge, and also to allow separate operation of mixing and aeration.
One such example may be the removal of nitrate nitrogen, which requires mixing of the wastewater without the introduction of air. The use of jet aerators is also advantageous for wastewater containing lime, which is produced in waste paper processing. The lime deposits clog membrane aerators at the bottom of the basin, which would have to compensate for the pressure loss with ever-increasing power. Replacing the membranes with jet aerators eliminates this problem. In addition, jet aerators carry more oxygen into the water, which can significantly increase COD removal in the same volume.
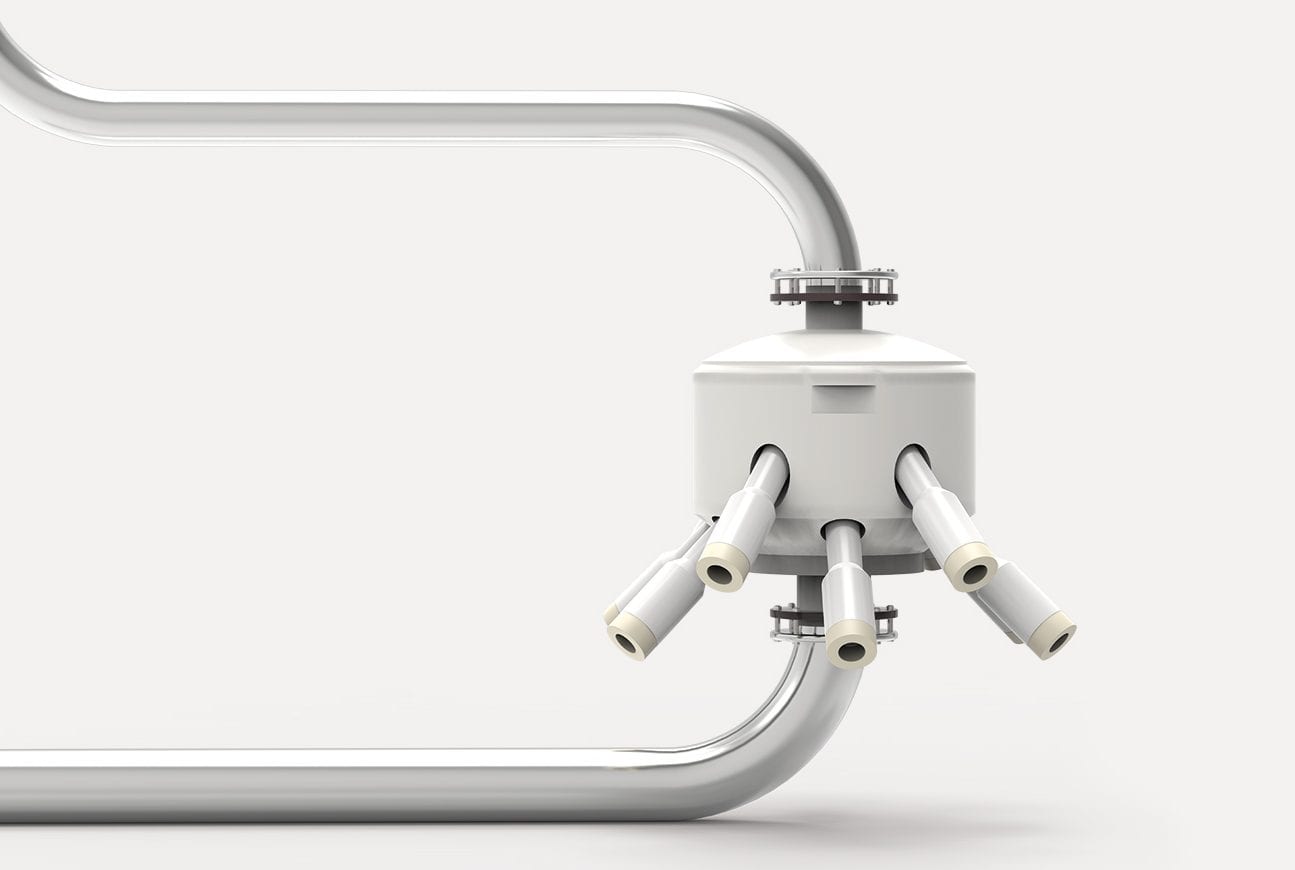

Your Advantages
- Strong circulation & efficient air intake (separately controllable)
- Special nozzle design effectively prevents sludge accumulation at the bottom & keeps solids in suspension
- Mobile solution enables maintenance during operation
- No moving parts → no special maintenance required
Other Wastewater Aeration Systems

Submersible Rotor Aerator
If the aeration of the wastewater is also to be combined with mixing of the biomass, submersible rotor aerators are established as active systems.
Perforated Tubes
For uncomplicated wastewater in high-load stages (MBBR), perforated pipes characterized by medium-bubble aeration are used.
Membrane aerator
If the laboratory analysis shows that the wastewater has a low lime content, membrane aerators are preferably used in the activated sludge plants.